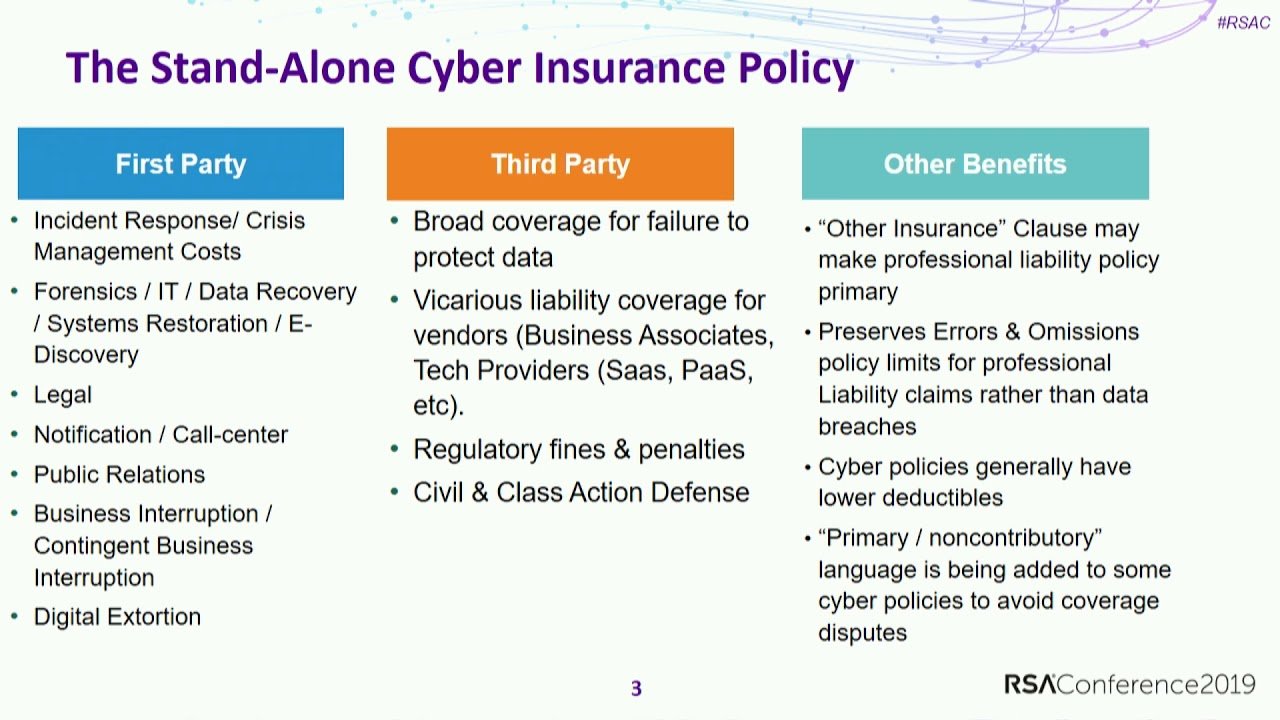
Beyond the Single-Family Dream: Exploring Alternative Real Estate Investments in the US
Beyond the Single-Family Dream: Exploring Alternative Real Estate Investments in the US
Single-family homes have long been the cornerstone of the American dream of homeownership. However, for investors, the real estate landscape offers a wealth of opportunities beyond detached dwellings. This blog delves into some of the most popular alternative real estate investments in the US, exploring their advantages and disadvantages to help you align your investment strategy with your financial goals.
Condominiums (Condos):
Condos are self-contained units within a larger, multi-unit building. Ownership typically extends to the interior walls of the unit, while common areas like hallways, lobbies, and grounds are shared with other condo owners.
Pros:
- Lower upfront cost: Compared to single-family homes, condos often have a lower purchase price, making them a good entry point for new investors.
- Less maintenance: Condo associations typically handle exterior maintenance, landscaping, and common area upkeep, freeing up your time and resources.
- Amenities: Many condo buildings offer amenities like pools, gyms, and security features, adding value to your investment.
- Potential for appreciation: Well-managed condo buildings can appreciate in value over time, offering good returns.
Cons:
- HOA fees: Homeowner association (HOA) fees cover maintenance and amenities, but they can be a significant ongoing expense.
- Less control: HOA rules dictate everything from renovations to pet ownership, limiting your control over the property.
- Shared amenities: Overcrowding of common areas or noisy neighbors can be a downside of condo living.
- Market fluctuations: Condo values can be more susceptible to market fluctuations compared to single-family homes.
Who should consider condos?
Condos are a good fit for investors seeking a low-maintenance, turnkey investment with potential for appreciation. They are ideal for busy professionals or retirees who don’t want the hassle of property upkeep.
Multi-Unit Properties (Duplexes, Triplexes, Fourplexes):
Multi-unit properties are buildings containing two or more separate residential units. You, as the owner, can rent out these units individually, generating multiple income streams. Common multi-unit options include duplexes (two units), triplexes (three units), and fourplexes (four units).
Pros:
- Strong rental income: Owning multiple units allows you to generate income from several tenants, potentially increasing your overall return on investment.
- Tax benefits: Depreciation allows you to deduct a portion of the property’s value from your taxable income each year.
- Build equity: Owning a multi-unit property allows you to build equity over time through rental income and potential appreciation.
- Hedge against vacancy: If one unit becomes vacant, you still have income coming in from the other units.
Cons:
- Higher upfront cost: Compared to condos, multi-unit properties require a larger initial investment.
- Increased management responsibilities: You’ll be responsible for tenant screening, maintenance, and repairs for multiple units. This can be time-consuming and require additional skills or hiring property management.
- Potential for vacancy: Vacancy in one or more units can significantly impact your cash flow.
- Financing challenges: Obtaining financing for multi-unit properties can be more complex compared to single-family homes.
Who should consider multi-unit properties?
Multi-unit properties are suitable for investors who want to maximize rental income and build equity. They require a more hands-on approach to management but offer the potential for higher returns.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs):
REITs are companies that own, operate, or finance income-producing real estate. You can invest in REITs by purchasing shares on a stock exchange, offering a more passive way to participate in the real estate market.
Pros:
- Liquidity: REITs are easily bought and sold on stock exchanges, providing greater liquidity compared to directly owning property.
- Diversification: REITs invest in a variety of real estate sectors, such as residential, commercial, or healthcare, offering diversification and reducing risk.
- Passive income: REITs are required by law to distribute a significant portion of their taxable income to shareholders as dividends, providing a steady stream of income.
- Professional management: REITs are managed by experienced professionals, eliminating the need for direct property management responsibilities.
Cons:
- Market volatility: REIT share prices can fluctuate with the stock market, leading to potential losses.
- Limited control: As a shareholder, you have no control over the selection or management of individual properties within the REIT.
- Tax implications: REIT dividends are typically taxed as ordinary income, which can be higher than capital gains taxes.
- Indirect exposure to real estate: While offering some benefits of real estate ownership, REITs don’t provide the same level of direct control and potential appreciation as owning physical property.
Who should consider REITs?
REITs are a good option for investors seeking:
- Passive income: A steady stream of income without the hassle of property management.
- Diversification: Exposure to the real estate market without the risks associated with owning individual properties.
- Lower investment barrier: An easier entry point into real estate investing compared to buying physical property.
Additional Considerations:
- REIT Types: Different REITs specialize in various property types. Residential REITs focus on apartments and housing, while commercial REITs invest in office buildings, shopping centers, or hotels. Consider your investment goals and risk tolerance when choosing a REIT type.
- Actively Managed vs. Index REITs: Actively managed REITs aim to outperform the market through strategic acquisitions and management. Index REITs track a specific market index, offering a more passive investment approach.
Beyond the Basics: Alternative Investment Options
- Real Estate Crowdfunding: Online platforms allow individuals to pool their money to invest in real estate projects. This approach offers fractional ownership in larger properties, potentially lowering the investment barrier. However, it carries higher risks due to the lack of direct control and the illiquidity of the investment.
- Real Estate Investment Groups: Joining a real estate investment group allows you to collaborate with other investors on larger projects. This can provide access to expertise and financing opportunities while spreading the risks and responsibilities.
- Fix-and-Flip Properties: Purchasing undervalued properties, renovating them, and reselling them for a profit can be a lucrative strategy. However, it requires significant renovation expertise, market knowledge, and the ability to handle unexpected costs and delays.
Choosing the Right Investment
The best alternative real estate investment for you depends on your individual goals, risk tolerance, and financial resources. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Investment goals: Are you seeking steady income, capital appreciation, or a combination of both?
- Risk tolerance: How comfortable are you with potential market fluctuations and property management challenges?
- Investment horizon: How long do you plan to hold onto the investment?
- Available capital: How much money are you comfortable investing upfront?
- Time commitment: Are you prepared to manage properties yourself, or will you hire property management?
Conclusion
The US real estate market offers a variety of investment opportunities beyond single-family homes. By understanding the pros and cons of condos, multi-unit properties, REITs, and other alternative options, you can develop a personalized investment strategy aligned with your financial goals. Remember, thorough research, due diligence, and consulting with a financial advisor are crucial steps before venturing into any real estate investment.
Additional Resources:
- National Association of Realtors (NAR): https://www.nar.realtor/
- Real Estate Investment Trust Institute (REIT Institute): https://www.reit.com/
- Crowdfunding Industry Regulation Authority (FINRA): https://www.finra.org/rules-guidance/guidance/reports/2022-finras-examination-and-risk-monitoring-program/funding-portal-crowdfunding
By exploring these resources and carefully considering your options, you can unlock the potential of alternative real estate investments and build a strong financial future.