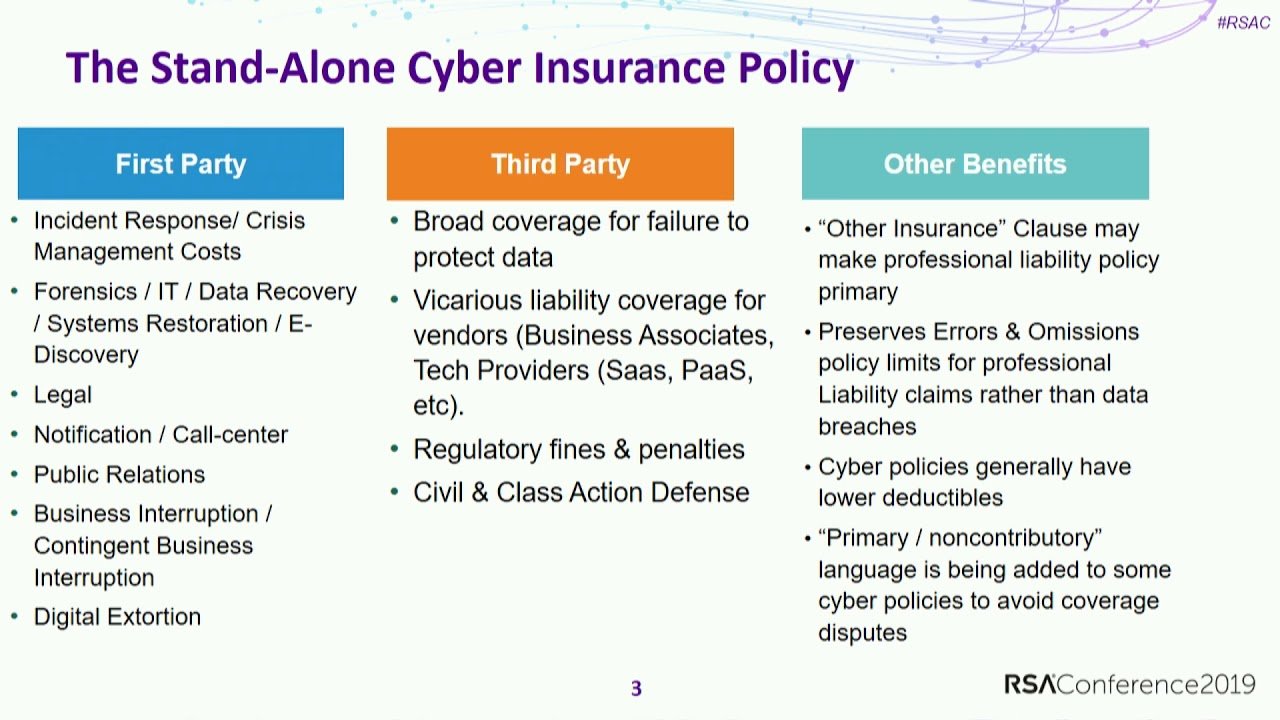
All Types of Insurance and Their Coverage
Demystifying Insurance Coverage in the US: A Guide to Staying Protected
Life in the US is full of unforeseen circumstances. From fender benders to medical emergencies, unexpected events can wreak havoc on your finances. That’s where insurance comes in – a safety net that helps you weather financial storms. But with so many types of insurance available, it can be overwhelming to navigate the options and choose the right coverage.
This blog post aims to demystify insurance coverage in the US. We’ll break down the four most common types of insurance – health, auto, home, and life – explaining what they cover, what’s excluded, and how to determine the right amount of coverage for your needs.
Understanding Insurance Basics
Before diving into specific types, let’s establish some fundamental insurance concepts:
- Policy: A legal contract between you (the insured) and an insurance company (the insurer). It outlines what’s covered, exclusions, and your responsibilities in case of a claim.
- Premium: The amount you pay periodically (monthly, yearly) to maintain your insurance coverage.
- Deductible: The amount you pay out of pocket before the insurance company starts covering your claim. Higher deductibles typically mean lower premiums.
- Coverage Limits: The maximum amount the insurance company will pay for a covered loss.
- Claim: A formal request you file with the insurance company to receive reimbursement for a covered loss.
Types of Insurance and Their Coverage:
1. Health Insurance
Health insurance protects you from the high costs of medical care. Here’s a breakdown:
-
What it Covers:
- Hospitalization (inpatient and outpatient care)
- Doctor visits
- Surgeries
- Prescriptions (depending on the plan)
- Preventive care (checkups, vaccinations)
-
Common Exclusions:
- Cosmetic surgery (unless medically necessary)
- Vision care (usually covered by separate vision insurance)
- Dental care (usually covered by separate dental insurance)
- Long-term care (nursing homes)
- Pre-existing conditions (may have limitations in some plans)
-
Choosing the Right Coverage:
- Consider your health status and how often you anticipate needing medical care.
- Choose a plan with a deductible and out-of-pocket maximum that fits your budget.
- Look for a network of doctors and hospitals covered by your plan to ensure you receive in-network benefits.
- Resources: Healthcare.gov (https://www.healthcare.gov/), National Association of Health Underwriters (http://welcometonahu.org/)
2. Auto Insurance
Auto insurance protects you financially in case of a car accident. Here’s a breakdown of the main coverages:
What it Covers:
-
Liability Coverage: This is mandatory in most states and covers injuries and property damage caused by you to others in an accident. It comes in two parts:
- Bodily injury liability: Pays for medical expenses of those injured in an accident you cause.
- Property damage liability: Covers damage to the other person’s vehicle or property.
-
Collision Coverage: Covers damage to your own car resulting from a collision with another vehicle or object.
-
Comprehensive Coverage: Covers damage to your car caused by events other than collisions, such as theft, fire, vandalism, hail, or animal strikes.
-
Uninsured/Underinsured Motorist Coverage (UM/UIM): Protects you financially if you’re hit by a driver with no insurance or inadequate insurance.
-
Medical Payments Coverage: Covers medical expenses for you and your passengers, regardless of who’s at fault in an accident.
-
Common Exclusions:
- Damage caused while driving under the influence of drugs or alcohol
- Racing or other intentional damage
- Normal wear and tear
-
Choosing the Right Coverage:
- The minimum required liability coverage varies by state. Consider your car’s value, your driving habits, and your risk tolerance when choosing collision and comprehensive coverage.
- UM/UIM coverage is highly recommended, especially in areas with high rates of uninsured drivers.
-
3. Homeowners Insurance (HOI):
-
What it Covers:
- Personal liability coverage: Protects you financially if someone gets injured on your property or you accidentally damage someone else’s property.
- Additional coverages (may vary by policy): Flood insurance, earthquake insurance, etc.
-
Common Exclusions:
- Floods (requires separate flood insurance)
- Earthquakes (may require separate earthquake insurance)
- Normal wear and tear
- Intentional damage
- Termite or pest damage (may require separate coverage)
-
Choosing the Right Coverage:
- Consider the value of your home and belongings to determine dwelling and personal property coverage amounts.
- Factor in your location’s risk factors for floods, earthquakes, or other perils.
- Evaluate your need for additional coverages based on your specific risks.
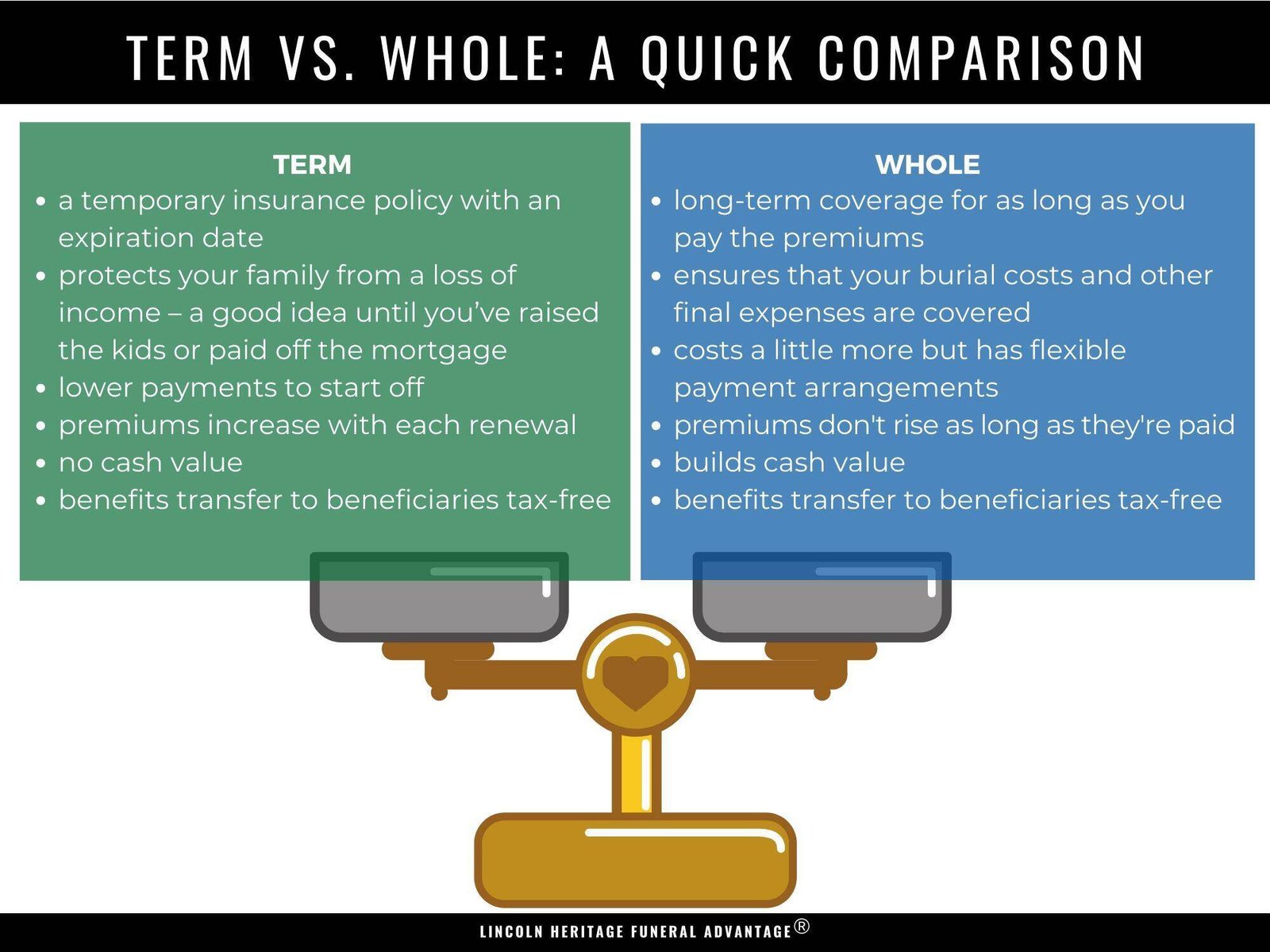
4. Life Insurance
Life insurance provides a financial benefit to your beneficiaries (designated loved ones) upon your death. Here’s a breakdown of the main types:
-
Term Life Insurance:
- Offers coverage for a specific period (e.g., 10, 20, 30 years).
- Typically cheaper than permanent life insurance.
- Pays a death benefit only if you die within the term.
-
Permanent Life Insurance:
- Offers lifelong coverage.
- Builds cash value over time, which you can borrow against or withdraw (depending on the policy).
- More expensive than term life insurance.
- Common types include whole life and universal life insurance.
-
Choosing the Right Coverage:
- Consider your financial dependents and how much they would need to cover expenses after your death.
- Decide if you want a policy with a cash value component.
- Term life insurance is suitable for temporary needs like young children, while permanent life insurance can provide long-term financial security.
Additional Considerations:
- Compare Quotes: Get quotes from multiple insurance companies before making a decision.
- Review the Policy Carefully: Understand the details of your policy, including coverage limits, exclusions, and claims process.
- Bundle Your Coverage: Many insurance companies offer discounts for bundling multiple policies (e.g., auto and home).
- Review Regularly: As your life circumstances change (marriage, children, buying a home), re-evaluate your insurance needs and update your coverage accordingly.
Remember: Insurance is a complex topic, and this blog post provides a general overview. It’s always best to consult with a qualified insurance agent or broker to discuss your specific needs and get personalized recommendations. They can help you navigate the different types of insurance, choose the right coverage amounts, and find the best rates.
By understanding insurance and choosing the right coverage, you can achieve peace of mind knowing you’re financially protected in case of unexpected events.
-